Мы расскажем Вам все об этом товаре, предложим наилучшие условия и ознакомим с подходящими акционными предложениями!
Оператор перезвонит Вам через 15-30 минут
Чтобы приобрести английский препарат «Король Ричард I», Вам нужно заполнить и отправить анкету, и наш специалист свяжется с Вами.
Прежде чем рекомендовать препарат к применению, мы должны быть уверены в том, что он действительно решит Вашу проблему.

Доставка
конфиденциальна
Чтобы узнать подробности о препарате и получить бесплатную консультацию специалиста, заполните заявку.
Если хотя бы два пункта - правда, Ваш организм «кричит» о помощи!

Активируются клетки иммунной системы макрофаги и «поедают» холестериновые бляшки в сосудах Приток крови в половой член восстанавливается.
Активируются клетки иммунной системы лимфоциты и устраняют вялотекущие инфекции. Снимается хроническое воспаление, включая пещеристые тела полового члена и простатит.
Активированные клетки иммунной системы макрофаги«поедают» клетки аденомы предстательной железы.
Отключается выработка вредоносным жиром внутри живота (висцеральным жиром) гормонов мужского старения. Среди них - мощный женский гормон эстрон. Препарат блокирует активность висцерального жира, прекращая разрушение яичек. Восстанавливается выработка ими главного мужского гормона тестостерона. Половое желание возвращается.

Препарат не вызывает привыкания и не содержит вредных веществ. Он полностью совместим с алкоголем.

Семяна гуараны
Препятствуют гормональной активности и уменьшают висцеральный жир.
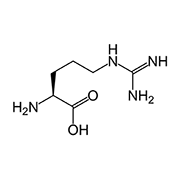
L-аргинин
Дает «мгновенный» эффект расширения сосудов полового члена за счет выработки оксида азота.

Экстракт корня имбиря
мощное противоопухолевое действие (аденома простаты)

Корейский женшень
мощное противоопухолевое действие (аденома простаты), «мгновенный» стимулирующий эффект

Перец стручковый острый
капсаицин обладает мощным противоопухолевым действием, борется с висцеральным жиром

Экстракт пажитника греческого
«отключает» гормональную активность висцерального жира, мощное противоопухолевое действие, мощное противодиабетическое действие

Экстракт пальмы Сереноа Репенс
прямое действие на аденому простаты. Экстракт пальмы Сереноа Репенс лежит в основе известного лекарства Простамол Уно

Натуральный кофеин из кофейных зерен
«мгновенное» общестимулирующее действие, повышение концентрации внимания на половом акте

Экстракт какао
«мгновенное» расширение сосудов полового члена
«КОРОЛЬ РИЧАРД I» ВЕРНУЛ ПОТЕНЦИЮ МИЛЛИОНАМ БРИТАНЦЕВ!
ОН ВЕРНЕТ ЕЕ И ВАМ!

МОЩНОЕ ДЕЙСТВИЕ КАЖДОГО КОМПОНЕНТА ПРЕПАРАТА ПОДТВЕРЖДЕНО СПИСКОМ МЕЖДУНАРОДНОЙ НАУЧНОЙ ЛИТЕРАТУРЫ.
ИСТОЧНИК:

Национальная Библиотека Здоровья США
ЧИТАТЬ ПОДРОБНЕЕ…
Ginger: A Novel Strategy to Battle Cancer through Modulating Cell Signalling Pathways: A Review.
1Department of Medical Laboratories, College of Applied Medical Sciences, Qassim University, Buraidah, Saudi Arabia.
Abstract
Numerous studies have been performed in understanding the development of cancer. Though, the mechanism of action of genes in the development of cancer remains to be explained. The current mode of treatment of cancer shows adverse effects on normal cells and also alter the cell signalling pathways. However, ginger and its active compound have fascinated research based on animal model and laboratories during the past decade due to its potentiality in killing cancer cells. Ginger is a mixture of various compounds including gingerol, paradol, zingiberene and shogaol and such compounds are the main players in diseases management. Most of the health-promoting effects of ginger and its active compound can be attributed due to its antioxidant and anti-tumour activity. Besides, the active compound of ginger has proven its role in cancer management through its modulatory effect on tumour suppressor genes, cell cycle, apoptosis, transcription factors, angiogenesis and growth factor. In this review, the role of ginger and its active compound in the inhibition of cancer growth through modulating cell signalling pathways will be reviewed and discussed.
Copyright© Bentham Science Publishers; For any queries, please email at epub@benthamscience.net.
KEYWORDS:
Ginger; antioxidant activity; antitumor activity; cell signalling pathway; gingerol; shogaol.
L-arginine as dietary supplement for improving microvascular function.
Abstract
BACKGROUND:
Reduced availability of nitric oxide leads to dysfunction of endothelium which plays an important role in the development of cardiovascular diseases.
OBJECTIVE:
The aim of the present study was to determine whether the dietary supplement L-arginine improves the endothelial function of microvessels by increasing nitric oxide production.
METHODS:
We undertook experiments on 51 healthy male volunteers, divided into 4 groups based on their age and physical activity since regular physical activity itself increases endothelium-dependent vasodilation. The skin laser Doppler flux was measured in the microvessels before and after the ingestion of L-arginine (0.9 g). The endothelium-dependent vasodilation was assessed by acetylcholine iontophoresis and the endothelium-independent vasodilation by sodium nitroprusside iontophoresis. In addition, we measured endothelium-dependent and endothelium-independent vasodilation in 81 healthy subjects divided into four age groups.
RESULTS:
After the ingestion of L-arginine, the endothelium-dependent vasodilation in the young trained subjects increased (paired t-test, p < 0.05), while in the other groups it remained the same. There were no differences in the endothelium-independent vasodilation after ingestion of L-arginine. With aging endothelium-independent vasodilation decreased while endothelium-dependent vasodilation remained mainly unchanged.
CONCLUSION:
Obtained results demonstrated that a single dose of L-arginine influences endothelium-dependent vasodilation predominantly in young, trained individuals.
KEYWORDS:
L-arginine; aging; endothelium-dependent vasodilation; endothelium-independent vasodilation; laser Doppler flux; nitric oxide; physical activity; skin microcirculation
Am Fam Physician. 2003 Oct 15;68(8):1539-42.
Panax ginseng.
1Program in Integrative Medicine, University of Arizona College of Medicine, Tucson, Arizona 85724, USA. dskseat@aol.com
Abstract
The herbal remedies referred to as "ginseng" are derived from the roots of several plants. One of the most commonly used and researched of the ginsengs is Panax ginseng, also called Asian or Korean ginseng. The main active components of Panax ginseng are ginsenosides, which have been shown to have a variety of beneficial effects, including anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and anticancer effects. Results of clinical research studies demonstrate that Panax ginseng may improve psychologic function, immune function, and conditions associated with diabetes. Overall, Panax ginseng appears to be well tolerated, although caution is advised about concomitant use with some pharmaceuticals, such as warfarin, oral hypoglycemic agents, insulin, and phenelzine. Panax ginseng does not appear to enhance physical performance. Products with a standardized ginsenoside concentration are available.
Biological Activities of Red Pepper (Capsicum annuum) and Its Pungent Principle Capsaicin: A Review.
1a Department of Biochemistry and Nutrition , CSIR-Central Food Technological Research Institute , Mysore , India.
Abstract
Capsaicin, the pungent alkaloid of red pepper (Capsicum annuum) has been extensively studied for its biological effects which are of pharmacological relevance. These include: cardio protective influence, antilithogenic effect, antiinflammatory, and analgesia, thermogenic influence, and beneficial effects on gastrointestinal system. Therefore, capsaicinoids may have the potential clinical value for pain relief, cancer prevention and weight loss. It has been shown that capsaicinoids are potential agonists of capsaicin receptor (TRPV1). They could exert the effects not only through the receptor-dependent pathway but also through the receptor-independent one. The involvement of neuropeptide Substance P, serotonin, and somatostatin in the pharmacological actions of capsaicin has been extensively investigated. Topical application of capsaicin is proved to alleviate pain in arthritis, postoperative neuralgia, diabetic neuropathy, psoriasis, etc. Toxicological studies on capsaicin administered by different routes are documented. Capsaicin inhibits acid secretion, stimulates alkali and mucus secretion and particularly gastric mucosal blood flow which helps in prevention and healing of gastric ulcers. Antioxidant and antiinflammatory properties of capsaicin are established in a number of studies. Chemopreventive potential of capsaicin is evidenced in cell line studies. The health beneficial hypocholesterolemic influence of capsaicin besides being cardio protective has other implications, viz., prevention of cholesterol gallstones and protection of the structural integrity of erythrocytes under conditions of hypercholesterolemia. Beneficial influences of capsaicin on gastrointestinal system include digestive stimulant action and modulation of intestinal ultrastructure so as to enhance permeability to micronutrients.
KEYWORDS:
Anti-inflammatory; Cancer preventive; Capsaicin; Cardio protective; Pain relief; Red pepper; Thermogenic; Vanilloid receptor
A small plant with big benefits: Fenugreek (Trigonella foenum-graecum Linn.) for disease prevention and health promotion.
1Department of Pharmaceutical Sciences, College of Pharmacy, Larkin University, Miami, FL, USA.
2Cepham Research Center, Piscataway, NJ, USA.
3Department of Pharmacological and Pharmaceutical Sciences, University of Houston College of Pharmacy, Houston, TX, USA.
Abstract
Plant-derived natural products have long-standing utility toward treating degenerative diseases. It is estimated that about two-thirds of world population depend on traditional medicine for primary medical needs. Fenugreek (Trigonella foenum-graecum Linn.), a short-living annual medicinal plant belonging to Fabaceae family, is used extensively in various parts of the world as herb, food, spice, and traditional medicine. Fenugreek is considered as one of the oldest medicinal plants and its health-promoting effects have been cited in Ayurveda and traditional Chinese medicine. The investigations into the chemical composition and pharmacological actions have seen a renaissance in recent years. Extensive preclinical and clinical research have outlined the pharmaceutical uses of fenugreek as antidiabetic, antihyperlipidemic, antiobesity, anticancer, anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, antifungal, antibacterial, galactogogue and for miscellaneous pharmacological effects, including improving women's health. The pharmacological actions of fenugreek are attributed to diverse array of phytoconstituents. The phytochemical analysis reveals the presence of steroids, alkaloids, saponins, polyphenols, flavonoids, lipids, carbohydrates, amino acids, and hydrocarbons. This review aims to summarize and critically analyze the current available literature to understand the potential of fenugreek for disease prevention and health improvement with special emphasis on cellular and molecular mechanisms. Current challenges and new directions of research on fenugreek are also discussed.
© 2017 WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim.
KEYWORDS:
Cancer; Diabetes; Health benefits; Phytochemicals; Trigonella foenum-graecum
Use of saw palmetto (Serenoa repens) extract for benign prostatic hyperplasia.
1Department of Food Science and Engineering, Ewha Womans University, 52 Ewhayeodae-gil, Seodaemun-gu, Seoul, 03760 Korea.
Abstract
Benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) is a noncancerous growth of the prostate. BPH commonly occurs in elderly men. Lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS) secondary to BPH (LUTS/BPH) have significant impacts on their health. Saw palmetto (Serenoa repens) extract (SPE) has been evaluated for its effectiveness in improvement of LUTS/BPH at preclinical and clinical levels. Potential mechanisms of actions include anti-androgenic, pro-apoptotic, and anti-inflammatory effects. However, SPE efficacy was inconsistent, at least partly due to a lack of a standardized SPE formula. A hexane extract (free fatty acids, > 80%) provided more consistent results. Free fatty acids (lauric acid) were effective in inhibition of 5α-reductase, and phytosterol (β-sitosterol) reduced prostatic inflammation. Multiple actions derived from different constituents may contribute to SPE efficacy. Evaluation of the clinical relevance of these bioactive components is required for standardization of SPE, thereby enabling consistent efficacy and recommendations for the use in the prevention and treatment of BPH.
© The Korean Society of Food Science and Technology 2019.
KEYWORDS:
Benign prostatic hyperplasia; Fatty acids; Phytosterol; Saw palmetto extract; Standardized formula
Curr Neuropharmacol. 2015 Jan;13(1):71-88. doi: 10.2174/1570159X13666141210215655.
Caffeine: cognitive and physical performance enhancer or psychoactive drug?
1Department of Anatomical, Histological, Forensic Medicine and Orthopedic Sciences, "Sapienza" University of Rome, Rome, Italy;
2NESMOS (Neuroscience, Mental Health, and Sensory Organs) Department, School of Medicine and Psychology, "Sapienza" University of Rome, Rome, Italy.
Abstract
Caffeine use is increasing worldwide. The underlying motivations are mainly concentration and memory enhancement and physical performance improvement. Coffee and caffeine-containing products affect the cardiovascular system, with their positive inotropic and chronotropic effects, and the central nervous system, with their locomotor activity stimulation and anxiogenic-like effects. Thus, it is of interest to examine whether these effects could be detrimental for health. Furthermore, caffeine abuse and dependence are becoming more and more common and can lead to caffeine intoxication, which puts individuals at risk for premature and unnatural death. The present review summarizes the main findings concerning caffeine's mechanisms of action (focusing on adenosine antagonism, intracellular calcium mobilization, and phosphodiesterases inhibition), use, abuse, dependence, intoxication, and lethal effects. It also suggests that the concepts of toxic and lethal doses are relative, since doses below the toxic and/or lethal range may play a causal role in intoxication or death. This could be due to caffeine's interaction with other substances or to the individuals' preexisting metabolism alterations or diseases.
KEYWORDS:
Abuse; caffeine; coffee; dependence; energy drinks; safety doses; toxicity
Phytother Res. 2016 Oct;30(10):1641-1657. doi: 10.1002/ptr.5665. Epub 2016 Jul 1.
The Impact of Cocoa Flavanols on Cardiovascular Health.
1Institute of Forensic Medicine, University of Freiburg, Albertstr. 9, 79104, Freiburg, Germany.
2Labor Signal Transduction, Department of Biomedicine, University Hospital, Hebelstrasse 20, 4041, Basel, Switzerland.
3Department of Nutritional and Food Sciences, Chair of Molecular Food Technology, University of Bonn, Römerstr. 164, 53117, Bonn, Germany.
4Institut Prof. Dr. Georg Kurz GmbH, Stöckheimer Weg 1, 50829, Köln, Germany.
5Institute of Forensic Medicine, University of Freiburg, Albertstr. 9, 79104, Freiburg, Germany. sigrun.chrubasik@klinikum.uni-freiburg.de.
Abstract
The aim of the study was to review the effect of cocoa flavanols on cardiovascular health, with emphasis on the doses ingested, and to analyze a range of cocoa products for content of these compounds. PubMed was searched from 2010 to locate systematic reviews (SR) on clinical effects of chocolate consumption. Thirteen SRs were identified and reviewed, and provided strong evidence that dark chocolate did not reduce blood pressure. The evidence was however strong for an association with increased flow-mediated vasodilatation (FMD) and moderate for an improvement in blood glucose and lipid metabolism. Our analysis showed that cocoa products with around 100 mg epicatechin can reliably increase FMD, and that cocoa flavanol doses of around 900 mg or above may decrease blood pressure in specific individuals and/or if consumed over longer periods. Out of 32 cocoa product samples analyzed, the two food supplements delivered 900 mg of total flavanols and 100 mg epicatechin in doses of 7 g and 20 g and 3 and 8 g, respectively. To achieve these doses with chocolate, around 100 to 500 g (for 900 mg flavanols) and 50 to 200 g (for 100 mg epicatechin) would need to be consumed. Chocolate products marketed for their purported health benefits should therefore declare the amounts of total flavanols and epicatechin.
Copyright © 2016 John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.
KEYWORDS:
mediated vasodilatation

БЫСТРЫЙ
ЗАКАЗ
Вы оставляете заявку
на сайте

БЕСПЛАТНАЯ
КОНСУЛЬТАЦИЯ
эксперта
Эксперт марки связывается
с Вами для подтверждения
заказа и подбора
индивидуального курса.

БЕСПЛАТНАЯ
ДОСТАВКА
Мы бесплатно доставляем
Вашу посылку
по указанному адресу.


ОПЛАТА
Вы получаете свой
заказ и платите за него
на почте или курьеру.

100% гарантия качества В России английский препарат «Король Ричард I» прошел все предписанные законом процедуры регистрации и контроля качества.
Гарантия
конфиденциальности
Мы гарантируем полную конфиденциальность при получении Вами заказа. Никто, кроме Вас, не узнает о содержимом упаковки.
Чтобы приобрести препарат «КОРОЛЬ РИЧАРД I», Вам нужно заполнить и отправить анкету, и наш специалист свяжется с Вами.
Прежде чем рекомендовать препарат к применению, мы должны быть уверены в том, что он действительно Вам поможет.

Доставка
конфиденциальна
Чтобы узнать подробности о препарате и получить бесплатную консультацию специалиста, заполните заявку.
Официальный дистрибьютор: «Международный центр здоровья»
127287, город Москва, Петровско-Разумовский проезд,
д. 29 стр. 4, этаж 1 помещ. I ком.28
ИНН 7713480994/771301001, ОГРН 1217700093159
Партнерская программа для вебмастеров


Спасибо!
Наш менеджер обязательно с вами свяжется.